CT Coronary Angiogram
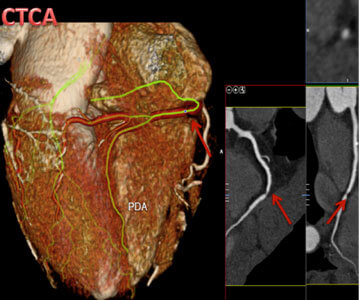
Example of CT Coronary Angiogram. Image on the left has both 3D/2D views and shows a severe narrowing in the right coronary artery (red arrow).
What is a CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA)?
CT Coronary Angiogram is sometimes called Cardiac CT, and can be abbreviated to CTCA. CTCA enables direct visualization and assessment of the blood vessels of the heart for any narrowing and vessel wall content (calcium or cholesterol deposit). It also allows the evaluation of structures within the heart and outside the heart such as the aorta. If a significant narrowing or blockage is visualised on the CTCA, your treating Cardiologist will most likely refer you for an invasive coronary angiogram to further assess the narrowing.
How is a CT Coronary Angiogram performed?
It is a non-invasive test that can be performed in a radiology centre with a specialised cardiac CT scanner.
Upon booking for CTCA, further detailed instructions will be given by the referred radiology practice at the time of booking. In general, you need to fast for 4 hours before test. You can take usual medications on the morning of the scan. In the radiology practice, you may be given extra cardiac medications to slow down the heart rate. During the scanning, intravenous contrast is injected to allow visualization of the coronary artery. The actual CT scanning time for the heart is around 2-5 minutes but most patients usually stay in the radiology practice from 1- 4 hours to ensure safety.
The CTCA images obtained is further post-processed and reported by a qualified Cardiologist and Radiologist. Both are experienced and accredited in interpreting CTCA images. Your Cardiologist will be notified of the results promptly if it is an abnormal study.
Why is a CT Coronary Angiogram performed?
CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA) is recommended when a functional study such as a stress test is unable to exclude heart vessel disease confidently or cannot be performed in a patient with cardiac symptoms. A normal CTCA study has very high accuracy in excluding any significant heart vessel disease. The information from a CTCA can be used to determine a patient’s risk of suffering a heart attack and detect other type of heart disease.
